'Cloud Computing', a buzz words that is frequently pops out in modern day discussions with IT professionals. Being a buzz word, Cloud Computing has proven to be a confusion term with respective to most IT fields. So, rather than 'defining' Cloud Computing, its worthy to write about how it has evolved during last few years and then go for the conceptual things on Cloud Computing.

Business App Nightmare
Nowadays, every modern business has an Enterprise Business Application as its backbone. For instance, for a given company, it may require a Business App, to manages its human resources and to support its business process in efficient manner. Traditional Business Applications are too complex and too expensive.

A traditional Business App often have most of these characteristics.
- Often required to have a dedicated datacentre and office space with power,cooling, bandwidth, network, servers and storage.
- Consists of a complicated software stack and required a team of exprets to install,configure and run the system.
- Required development,testing, staging, productions and fail-over environments.
- In case of a failure in any of these systems, we have to go for expensive commercial support and yet we can't guarantee that our prolem will get solved in time, without affecting our businees.
- When new versions comes out, it very likely to bring the whole system down for sometime for inhereient incompatibilities
- This is just for one single Business App, but imagine what would happen with multiple business apps.
- Organization concentrate more on the Business App rather than the business itself.
So, obviously we can't live with such traditional Business Aplication in this dynamic and competitive business world. We need a better and hassle free way of running our business. And that's where the 'Cloud Computing' comes to save us.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is a technology that uses the internet and central remote servers to maintain data and applications. It provides on demand resources and services over the internet with the power of scalability and reliability.
In simple terms, when you are using cloud computing, you don't need to install the required application on your system. Instead, you use the application that runs on a remote location/datacenter which we called the 'Cloud'. You just login, customize and start using it.
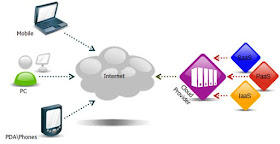
Gmail is the perfect example of Cloud Computing. You don't need a software system or mail server to send/receive emails. You just login to it, customize it and start using it. Unlike other traditional email management systems like MS Exchange, Gmail doesn't requires a software system, mail server, regular upgrades or dedicated team to manage it. Instead, everything is placed in the Cloud (and Cloud have all those things) and the users get all the benifits that are provided 'as a service'.
Cloud Computing for Enterprises
In the context of the Enterprises, all the traditional application that required in enterprises like HR,CRM and accoundintg apps can be cloudify. Which means that, running them on a cloud and any given business can customize it and use it in their allocated workspace.
Here we use the concept of 'Multitenancy', where a single instance of the software runs on a server, serving multiple clients(tenants).
So for instance, say a Enterprise Cloud App runs on a cloud and different businesses (tenants) are using it.
In this case, every business use the same enterprise cloud application, but it is flexible enough to everyone to customize it with their different requirements. Also version upgrades is no more a hassle for us, as they are upgraded automatically and our system becomes more reliable, more scalable and more secure.
Cloud Computing Models
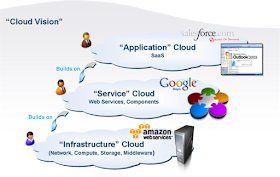
Software as a Service (SaaS)
This is the most widely used Cloud Computing approach to date. A business application can be run on the centralized servers(cloud) rather than running them on on-site servers/software systems. On Demand
Software as a service, delivers a single application through the browser to thousands of customers using a multitenant architecture. In the cloud service side, it only requires to maintain and manage one application on the cloud and in the client side, there are no any need of upfront investing on servers, software and license etc.
Salesforce, Google, NetSuit, Taleo, Concur Technologies
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS delivers development environments as a service. You build your own applications that run on the provider's infrastructure and are delivered to your users via the Internet from the provider's servers.
Salesforce's platform, Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2), Google App Engine, Coghead, Yahoo pipes, Windows Azure
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Infrastructure as a Service, is very much the backbone of the entire cloud computing concept. A well known examples include, Infrastructure vendors environments like Google gears which allow users to build applications and Cloud storages, such as Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) which allows user to store and retrieve any amount of data, at any time, from anywhere on the web.
Google Gears, Amazon S3
Cloud Computing Deployment Models
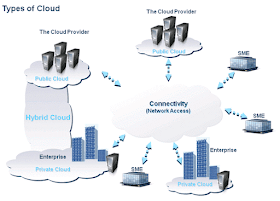
Public Clouds
In a public clouds, the services and infrastructure are provided off-site over the Internet. These clouds offer the greatest level of efficiency in shared resources; however, they are less secured and more vulnerable than private clouds.
Private Clouds
Unlike public clouds, in the Private Clouds, the services and infrastructure are maintained on a private network. These clouds offer the greatest level of security and control. However they require the company to still purchase and maintain all the software and infrastructure.
Hybrid Clouds
A hybrid cloud includes a variety of public and private options with multiple providers.
Pricing Schema
Cloud computing is often offered with a pricing model that lets you pay as you go and for just the services that you need. No capital expenditure is required.
Next big thing..

source: salesforce
Author: Kasun Indrasiri, Senior Software Engineer, WSO2 Inc



